The phylogeny of marine sculpins of the genus Icelinus with comments on the evolution and biogeography of the Pseudoblenninae.
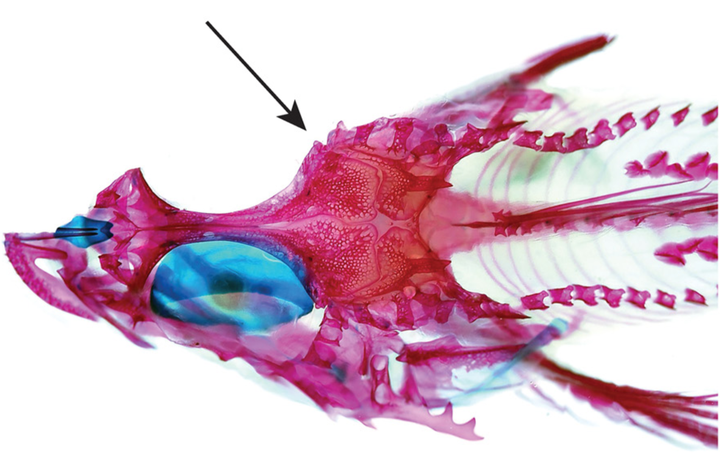 Figure 2C
Figure 2C
Abstract
The marine sculpins (Psychrolutidae) are a diverse percomorph family with notable morphological variation and repeated biogeographic patterns within the group. The psychrolutid genus Icelinus is unusual because it is one of the few near-shore members of the family that exhibits a trans-Pacific distribution; it has two species in the western Pacific and nine species in the eastern Pacific. Furthermore, the placement of Icelinus has been more inconsistent across molecular and morphological analyses than many genera. Previous phylogenetic studies have hypothesized sister taxa to Icelinus ranging from Antipodocottus, Chitonotus, and Stlengis, to a mixed clade of psychrolutids. The varied placements across these studies may be due to limited taxon sampling within Icelinus, and previous authors have never included western Pacific species of Icelinus in their analyses. This study tests the monophyly of the genus, examines the relationships between eastern and western Pacific species of Icelinus, and explores the relationships of Icelinus within Psychrolutidae. Our results show that the traditional grouping of Icelinus is polyphyletic. The eastern Pacific species of Icelinus are restricted to a clade sister to Furcina and Antipodocottus. The western Pacific species of Icelinus are recovered sister to the genus Stlengis. Given the polyphyly of Icelinus, the sister-group pairing of western Pacific species of Icelinus and Stlengis, as well as morphological similarity between the two groups, we recommend treating the western Pacific species of Icelinus as members of the genus Stlengis. With this taxonomic change, species in the genus Icelinus are now limited to the eastern Pacific, ranging from Alaska to Mexico.
Almetric and Dimension badges